DIY Power Measurement Module for Arduino
DESCRIPTION
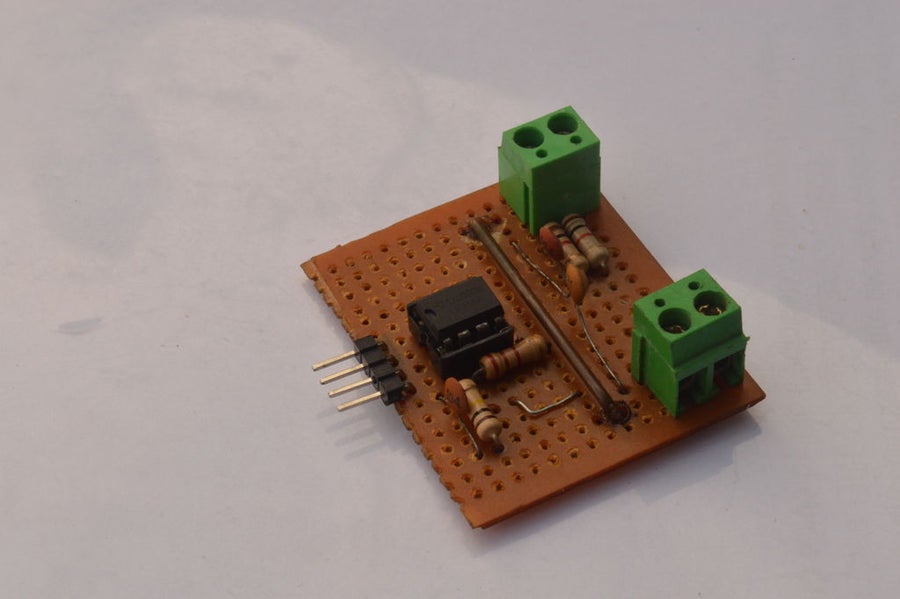
Hello everyone, I hope you are doing great! In this instructable I am going to show you how I made this Power meter/ Wattmeter module for use with an Arduino board. This power meter can calculate the power consumed by and DC Load. Along with power, this module can also give us accurate readings of voltage and current. It can easily measure low voltages (around 2V) and low currents, as low as 50 mA with an error not more than 20mA. The accuracy depends upon the choice of components based upon your requirements.
Supplies:
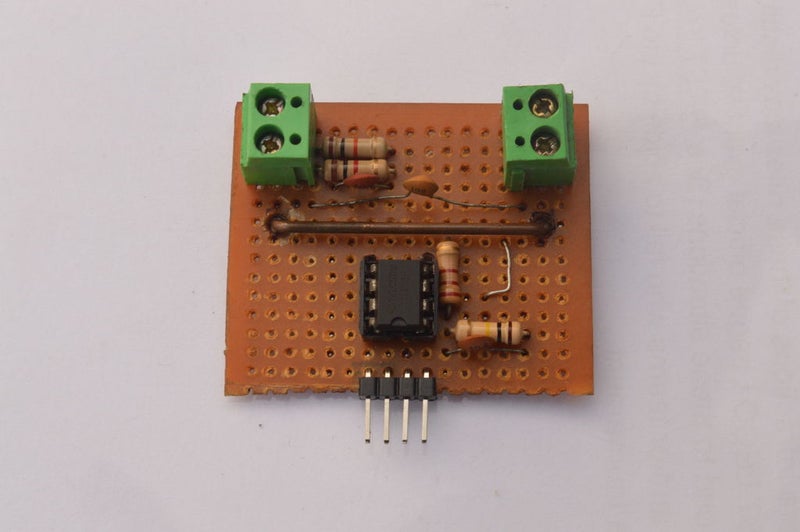
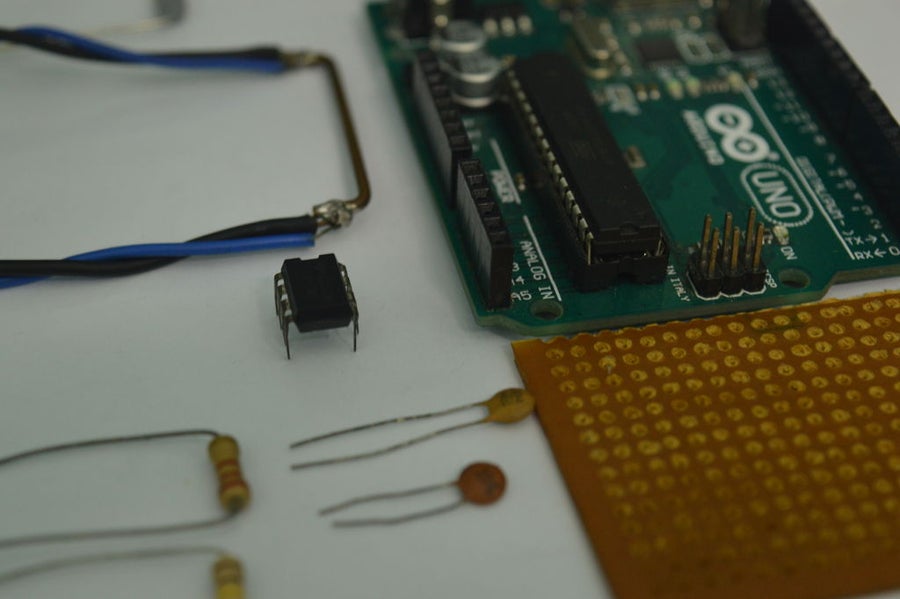
- IC LM358 dual OP-AMP
- 8 pin IC base
- Shunt resistor(8.6 milliOhms in my case)
- Resistors: 100K, 10K, 2.2K, 1K (1/2watt)
- Capacitors: 3 * 0.1uF ceramic capacitors
- Veroboard or zero board
- Screw terminals
- Soldering iron and solder
- Arduino Uno or any other compatible board
- OLED Display
- Connecting breadbard wires
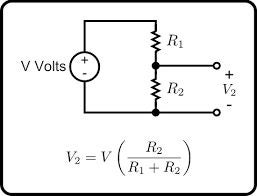
The working of the power module is based upon two concepts of circuit theory and basic electricity : The voltage divider concept for measurement of the input voltage and the Ohm's Law to calculate the current flowing through the circuit. We are using a shunt resistor to create a very small voltage drop across it. This voltage drop is in proportion to the amount of current flowing through the shunt. This small voltage when amplified by an operational amplifier can be used as an input to a microcontroller which can be programmed to give us the current value.The operational amplifier is used as a non inverting amplifier where the gain is determined by the values of the feedback resistor R2 and R1. Using the non inverting configuration allows us to have a common ground as the measuring reference. For this, the current is being measured on the low side of the circuit. For my application I have chosen a gain of 46 by using 100K and 2.2K resistor as feedback network. The voltage measurement is done by using a voltage divider circuit which divides the input voltage in proportion to the resistor network used.
Both the current value from the OP-Amp and the voltage value from the divider network can be fed into two analog inputs of the arduino so that we can calculate the power consumed by a load.
With the voltage and current sense networks connected and soldered, its time to solder the male header pins and make the necessary connections of power and signal outputs. The module will be powered by the standard operating voltage of 5 volts which we can easily get from an arduino board. The two voltage sense outputs will be connected to the analog inputs of the arduino.
I have attached the circuit diagram and code of the power module in this step( Previously I had attached the .ino and .txt file containing the code but some server error caused the code to be inaccessible or unreadable to users, so i wrote the entire code in this step. I know that's not a good way to share the code :( ). Feel free to modify this code according to your requirements. I hope this project was helpful for you. Please share your feedback in the comments. Cheers!
#include<SPI.h >
#include<Wire.h >
#include<Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include< Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#define OLED_RESET 4 Adafruit_SSD1306 display(OLED_RESET);
float val=0;
float current=0;
float voltage=0;
float power=0;
void setup() {
pinMode(A0,INPUT);
pinMode(A1,INPUT);
display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C); // initialize with the I2C addr 0x3C (for the 128x32) display.display();
delay(2000);
// Clear the buffer.
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(0, 0);
display.setTextColor(WHITE);
Serial.begin(9600); // To see the values on the serial monitor
}
void loop() {
// taking the average for stable readings
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
current=current + analogRead(A0);
voltage=voltage + analogRead(A1); }
current=(current/20); current=current * 0.0123 * 5.0; // calibration value,to be changed according to components used
voltage=(voltage/20); voltage=voltage* 0.0508 * 5.0; // calibration value,to be changed according to components used
power= voltage*current;
//printing the values on the serial monitor
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(power);
// printing the values on the OLED display
display.setCursor(0, 0);
display.print("Voltage: ");
display.print(voltage);
display.println(" V");
display.setCursor(0, 10);
display.print("Current: ");
display.print(current);
display.println(" A");
display.setCursor(0, 20);
display.print("Power: ");
display.print(power);
display.println(" W");
display.display();
delay(500); // refresh rate set by the delay
display.clearDisplay();
}








 2 More Images
2 More Images